UMN
|
LMN
|
|
Bulk
|
Normal till disuse atrophy
|
Prominent weakness and atrophy
occurs early
|
Tone
|
Increased
Except in spinal shock where
tone will be flaccid and recovers in around 2 weeks
|
Always HYPOTONIA
|
Power
|
Reduced, tends towards normal
over period of time if adequate stimulation maintained
|
Severely decreased
|
Abnormal movement
|
Fasciculation are not usually
seen
|
Fasciculation is due to
degenerative process in anterior horn cell
|
Reflexes
|
Brisk
|
Decreased to absent
|
Plantar/ Babiknsi
|
Up going
|
Downgoing
|
The most important
thing to know is the intactness of the muscle stretch reflex. The tone is
maintained under the influence of gamma motor neuron by the alpha motor neuron
and the bulk and power is the pure function alpha motor neuron. The reflex is
complete if its loop is complete.
 |
| Muscle Reflex arc |
Upper Motor
Neuron lesions are the lesion occurring anywhere in the central nervous system
from the brain upto the spinal cord before the alpha motor neurons arise from
the spinal cord. The lesion could arise from the cerebral cortex, internal capsule,
midbrain, pons, medulla and the cortico spinal tract in the spinal cord. The
lesions can be anything from vascular, traumatic, degenerative, and
inflammatory to infective.
The lesions occurring
after the alpha motor neuron accounts for the lower motor neuron lesions. The
lesions could arise in the nucleus of alpha motor neuron (Polio myelitis,
Amylotrophic lateral Sclerosis, brown sequard syndrome), Lesions in the nerve (Traumatic
resection, entrapement, neuritis), Lesion in the NMJ (Myasthenia gravis,
Lambert Eaton Syndrome) and the muscle (Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy, Beckers
Muscular Dystrophy )itself.
The two
principle that determine the features of upper motor and lower motor neuron
include the completeness of muscle reflex arc and the higher motor control over
it.
The motor reflex arc consists of the Ia fibres carrying the signal from muscle
spindle which prevents the excessive stretch of muscle by contracting it. The
afferent fibres mono synaptically fires the alpha motor neurons at the anterior
horn and causes the muscle contraction. This reflexes is controlled further by
higher centre and is thus there is an inhibitory mediatory released via an
intermediate neuron coming from the corticospinal tract. If this closed loop of
nerve are intact the muscle tendon reflex is intact and so is the deep tendon
reflex which is elicited using reflex hammer.
The tone is
the inherent state of contraction of muscles to maintain the posture of the
body. It is in medicated by the Gamma motor neuron coming together wit alpha
motor neuron and innervates the intrafusal fibres of muscle spindle and thus
increases the sensitivity of change in length of the muscle. It is also
directly innervated from the corticospinal tract and thus is affected in
response to UMN lesion. Along with that
the gamma motor neurons are spontaneously firing and thus influence the
sensitivity of alpha motor neurons and thus affect the tone.
In lower motor
neuron lesion, the alpha motor neuron and distal is injured. So the loop can
not be complete and hence no reflex contraction of muscle in response to stretch
of muscle spindle receptor. In upper motor neuron lesion, the higher inhibition
over the reflex arc is lost. This causes the excessive firing from alpha motor
neuron and hence exaggerated deep tendon reflex.
The lower
motor neurone lesion will develop flaccid paralysis because there is no
innervation to muscle fibre to cause its contraction and hence they easily go
into disuse atrophy early and the bulk is reduced. Contrary to the Upper motor
neuron lesion where the higher control of the muscle is lost but still the
muscle can be contracted locally. So, constant use of muscle via passive movement
can preserve the bulk of the muscle.
The tone in
upper motor neuron lesion is exaggerated because the supraspinous modulation
over the gamma motor neuron is lost and they are firing spontaneously. This increases the tone of the muscle with
increases sensitivity of muscle spindle to passive stretch and increased firing
in the Ia fibres. This increased firing induces increased firing in alpha motor
neuron and increased contraction.The tone is higher in the antigravity muscle
and hence clasp knife rigidity is due to the greater bulk of the antigravity
muscles and hence the paralysis is spastic type in upper motor neuron lesion.
However, in
the lower motor neuron lesion , again the same nerve that complete the muscle
reflex is incomplete and hence the normal tone is present due to absence of
innervation in the muscle to bring about the contraction and hence the tone is flaccid
and hence the paralysis flaccid paralysis.
In LMN lesion,
the muscle become hypersensitive to neurotransmitter as it is denervated.
Similarly the damaged lower motor erratically discharges the neurotransmitter
stored within itself as the neuron degrades. So, both increased hypersensitivity
and erratic release of neurotransmitter causes fasciculations. However, in UMN
lesion, there is regular firing to prevent the atrophy of muscles.
Learn about Cranial nerve examinations
Learn about Cranial nerve examinations
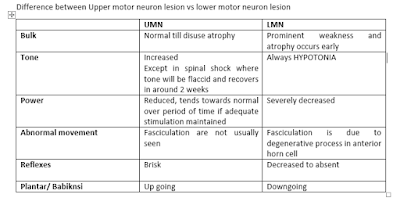 |
| Difference between UMN and LMN lesion in tabulated form. |
very good and clearly explained article.....kudos mate
ReplyDeleteI recently came across your blog and have been reading along. I thought I would leave my first comment. I don’t know what to say except that I have enjoyed reading. Nice blog, I will keep visiting this blog very often. health
ReplyDelete