Cesarean Section is the delivery of the product of
conception after the period of viability by making an incision in the anterior wall
of the Uterus.
Cesarean section step by step procedure (Flowchart)
Points to be noted are
Cesarean section step by step procedure (Flowchart)
 |
| Indication for Cesarean Section: Mnemonic |
Points to be noted are
1.
Product of Conception can be living or dead.
2.
Before viability, if POC is removed by
undergoing surgical Procedure it will be called Hyste-RO-tomy (Not Hyste-REC-tomy)
and not caesarean section.
3.
The delivery is made by making an incision on
the anterior wall of the UTERUS. Though incision on anterior wall of the
ABDOMEN is necessary to reach the anterior wall of uterus, the definition of cesarean
section will be incomplete just by mentioning the anterior abdominal wall. So
delivery of ruptured uterus and abdominal pregnancy is not C section.
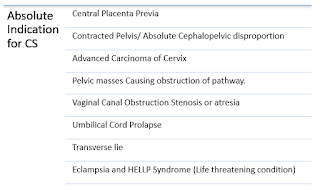 |
| Absolute Indication For C Section |
Absolute Indications for Cesarean section.
1.
Central Placenta Previa
2.
Contracted Pelvis/ Absolute Cephalopelvic
disproportion
3.
Advanced Carcinoma of Cervix
4.
Pelvic masses Causing obstruction of pathway.
5.
Vaginal Canal Obstruction Stenosis or atresia
6.
Umbilical Cord Prolapse
7.
Transverse lie
8.
Eclampsia and HELLP Syndrome (Life threatening
condition)
Learn about history taking in Obstetrics.
Learn about history taking in Obstetrics.
Relative Indications
1.
Relative Cephalopelvic Disproportion
2.
Previous Cesarean section
a.
Two previous C Section
b.
Scar dehiscence
c.
Previous CS was for recurrent condition
d.
Previous Classical CS
3.
Dystocia
a.
Power: Poor effort by mother, inefficient uterine
contractions
b.
Passage: CPD
c.
Passenger:
Large Fetus,
4.
Fetal Distress
a.
Non Reassuring CTG
b.
Fetal Asphyxia and acidosis
5.
Antepartum Hemorrhage
a.
Placenta Previa (type IIb,III)
b.
Abruptioplacentae
6.
Malpresentation
a.
Primi Breech
b.
Non Frank Breech
c.
Brow
d.
Shoulder
7.
Failed Progression of Labor
a.
Secondary Arrest
b.
Prolonged Labor
c.
Failed Instrumental Delivery
8.
Failed Induction of labor (Drugs, Artificial Rupture
of Membrane)
9.
Bad Obstetrics history
10.
Hypertensive Disorders
a.
Severe Preeclampsia
b.
Eclampsia
11.
Infections
a.
Chorioamnionitis
b.
HPV (Condyloma Acuminata)
c.
HIV
12.
Multifetal Pregnancy
a.
Mono amniotic twin
b.
Conjoint Twins
13.
Gynecological Illness
a.
Mechanical Obstruction due to Benign or
Malignant pelvic tumor
b.
Following repair of VVF (vesicovaginal Fistula)
14.
Medical Conditions
a.
Uncontrolled Diabetes Mellitus
b.
Heart Disease (Rheumatic/ Congenital/ Coarctation
of aorta)
c.
Marfan Syndrome

No comments:
Post a Comment