Enlargement of the size of the
spleen beyond its normal shape and size and position is defined as
splenomegaly. The normal anatomy of spleen is defined as a structure of 1inch x
3 inch x 5 inch, with weight of 7 ounces (~150-200g) in size and spans across
9-11 ribs in the left upper quadrant of the abdominal cavity. This is the rule
of odd number in spleen (1, 3, 5, 7, 9, and 11).
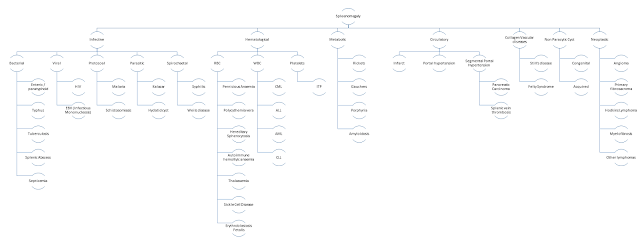 |
| Etiological Causes of Splenomegaly |
The size of the spleen has to increase by at least 500g to called splenomegaly and has to be more than 1000g to define as massive splenomegaly. It is not necessary that every enlarged spleen will be palpable by clinical examination. The size of the spleen has to increase by 3-5 folds to be appreciated clinically. In terms of size it has to be greater than 10-11 cm in its greatest diameter to be defined as moderate splenomegaly and more than 20 cm in its largest dimension to be called as massive splenomegaly.
The cause of splenomegaly can be
classified as either etiological causes or pathological cause.
Dividing the causes of
splenomegaly etiologically, it could either be infective, hematological, metabolic,
collagen vascular disease or other various causes. The most important one are obviously
the infective and the hematological causes.
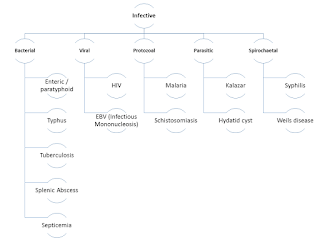 |
| Infective causes of splenomegaly |
Bacteria such as salmonella typhi/paratyphi, scrub typhus,
mycobacterium tuberculosis, pneumococcal splenic abscess and septicemia by any
organism can cause splenomegaly. HIV and EBV (infectious mononucleosis) are the
viral causes of splenomegaly. Malaria and Schistosomiasis are few tropical protozoal
disease to cause splenomegaly. Parasites
like Leshmania donovani (kalazar) and echinococcus (hydatid cyst) are other
causes. Syphilis and Weils (Leptospirosis) disease are some spirochetal
conditions associated with splenomegaly.
 |
| Hematological causes of splenomegaly |
Hematological causes may be related to RBC, WBC or platelet. The
condition where there is massive RBC destruction or massive extra medullary
hemopoeisis is associated with splenomegaly. Most of the hemolytic causes of
anemia such as hereditary spherocytosis, autoimmune hemolytic anemia,
thalassemia, sickle cell disease, erythroblastosis fetalis have splenomegaly.
Similarly faulty RBC synthesis in pernicious anemia leads to increased load in
spleen to cause hemolysis. The polycythemia is associated with increased extra
hemopoeitic synthesis of RBC. The Leukemia
including CML, ALL, AML, CLL will
have splenomegaly. ITP also has splenomegaly.
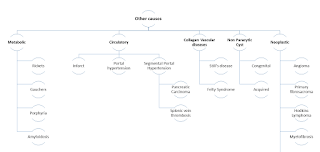 |
| Splenomegaly Causes other than infection and blood related |
Metabolic causes such as rickets, Gaucher’s, porphyria, amyloidosis
present with enlarged spleen clinically.
Infarction of spleen, portal hypertension associated with pancreatic
carcinoma and splenic vein thrombosis are some of the circulatory or vascular
causes. Collagen vascular diseases as Still's
disease and Felty syndrome are other causes. Non paracytic cyst either congenital
or acquired cause splenomegaly.
Angioma , primary fibrosacroma, Hogdkins lymphoma, myelofibrosis
are other lymphomas are the neoplastic
causes of the condition.
health
ReplyDeleteIt’s fascinating how many different conditions can lead to splenomegaly — especially the overlap between hematologic and infectious causes. I recently learned more about what doctor treats splenomegaly, and it’s surprising how multidisciplinary the evaluation can be.
ReplyDelete