The temporal bone fracture are common with head injury accounting for 30 % of all head trauma and 75 % of all motor vehicle accident. 31% of temporal bone fracture are associated with Motor vehicle accident.
Longitudinal fracture are common fracture caused by lateral forces over the mastoid and temporal squamosa and fracture line parallels petrous pyramid axis. It is generally anterior and extra-labyrinthine.
NEURAL SYMPTOMS WITH TRANSVERSE #
PHYSICAL SYMPTOMS WITH LONGITUDINAL #
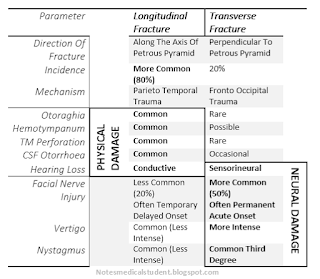 |
| Difference between temporal bone fracture types: Longitudinal Vs Transverse |
Nerve Injury or neural component more common with transverse # Facial nerve injury(VII), vertigo(VIII: Vestibular Nerve), Sensorineural hearing loss(VIII: Auditory Nerve) and Nystagmus (vestibular Nerve/ CNS component) are more common and intense with transverse fracture.
Physical damage like bleeding demonstrated as Hemotympanum and otorraghia , fractures seen as CSF otorrhea, Conductive hearing loss due o disruption of ossicles and Tympanic membrane perforation, are common with longitudinal fracture. Neural component less common or less intense than it’s contrary.
Parameter
|
Longitudinal
Fracture
|
Transverse
Fracture
|
||
Direction
Of Fracture
|
Along The Axis Of Petrous Pyramid
|
Perpendicular To Petrous Pyramid
|
||
Incidence
|
More Common (80%)
|
20%
|
||
Mechanism
|
Parieto Temporal Trauma
|
Fronto Occipital Trauma
|
||
Otoraghia
|
PHYSICAL DAMAGE
|
Common
|
Rare
|
|
Hemotympanum
|
Common
|
Possible
|
||
TM Perforation
|
Common
|
Rare
|
||
CSF
Otorrhoea
|
Common
|
Occasional
|
||
Hearing
Loss
|
Conductive
|
Sensorineural
|
NEURAL DAMAGE
|
|
Facial
Nerve Injury
|
Less Common (20%)
Often Temporary
Delayed Onset
|
More Common
(50%)
Often Permanent
Acute Onset
|
||
Vertigo
|
Common (Less Intense)
|
More Intense
|
||
Nystagmus
|
Common (Less Intense)
|
Common Third Degree
|
No comments:
Post a Comment