Notes of how to write history, examine a patient, tips and tricks, mnemonics, table of differences and other common things your examiner will ask you in exams and also in your morning rounds.
Search This Blog
Sunday, December 18, 2016
Sunday, September 4, 2016
Paediatrics: Head Examination: Differential Diagnoses
 |
| Causes of Delayed Dentition |
Delayed Closure of Sutures
 |
| Causes of Delayed Closure of suture |
Bossing of Skull
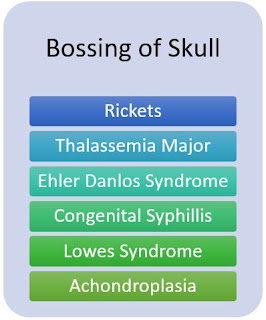 |
| Causes Of Bossing Of Skull |
Bulging Anterior Fontanelles
 |
| Causes of Bulging Anterior Fontanelle |
 |
| Causes Of Craniotabes |
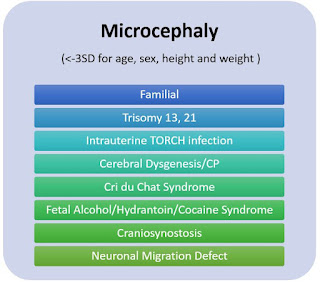 |
| Causes of Microcephaly |
>>Know the normal head circumference and its rate of growth.
Labels:
Bossing,
Craniotabe,
Delayed,
Dentition,
Differential diagnoses,
fontanelle,
Gum Hyperplasia,
head examination,
image,
List,
Macrocephaly,
Macroglossia,
Major,
Micropehaly,
paediatrics,
Skull,
Sutures
Monday, August 15, 2016
APPLYING FOR NMC EXAM : THE ADMIT CARD, EXAM AND RESULT
THE ADMIT CARD AND EXAM
How to get admit card?
Once you have submitted all
your documents and made the payment, your application will be processed. After
the last day of submission of application form, when you login into your
account it will show it as processed.
Then you will get “get the Admit card” option. On clicking that
your admit card will come.
How many copies to print ?
Two copies
Which photo to paste?
Hard copy of the one which you have uploaded in the website
while applying. It need not be same as that you pasted while getting your
provisional form.
What else need to be done?
Sign over the designated location and also over the original
photograph you have pasted.
Put the thumb print over the designated place.
How does it look like?
What is important in this card?
Bar code is the most important thing. They will scan it and
check it while you appear for exam. So if bar code is not printed may be try
again with better printer.
What is your ID ?
The number beneath the barcode is your id.
What else do I need to take while appearing for exam?
Nothing. Just one id card (Citizenship certificate original)
if possible along with the admit card.
Where is the centre?
Generally at Nepal Army Medical College at sanobharyang.
Follow link for map.
What is the timing ?
If they follow the same schedule as done previously then Reach
there by 07:30 as far as possible. Exam starts at 0900 am. Earlier you reach
more advantage you have in processing, finding seats and such things. Better
verify venue and timing before every exam by asking at NMC or viewing its main
page. nmc.org.np
How is the exam ?
There are enveloped sealed with your names printed over it.
How many sets?
I found there were a total of 5 sets at the time appeared. But
you can not be sure any one around you will have the same set.
Will your friends be around you ?
If you are lucky and have submitted the forms together. Because
there was issue with our PROVISIONAL certificate every one of my batch mate
submitted on the extended date and hence all were in same room with just one
extra person in between. if you want to be together make sure you guys submit in some random day together and not on the last day .
How many people in a class ?
My class and classes surrounding me had 15 in each. If your
room is in poly technical institute then surely there will be not more than 15
of them in a single class.
You must...
1. bring admit card to the examination centre.
2. leave the personal belonging outside the hall at own risk.
3. arrive test centre well ahead of scheduled exam time so that you will be able to find out that you seat location.
4. fill the answer sheets as per instruction on them.
5. sign the attendence sheet showing admit card.
6. handover the question booklet and answer sheet to the invigilator before leaving the hall.
You must not...
1. be late for more than 15 minutes after the commencement of exam, if you arrive late:
- you may not be admitted to the hall.
- you may not allowed to take any of the test components.
- you may not be eligible for refund.
2. carry any type of electronic device(e.g. mobile, calculator, pager, Ipod, pen drive, etc.)
3. bring any paper (blank/ written), instrument box and carry bags.
4. talk or disturb any candidate.
5. lend anything to, or borrow anything from, another candidate during the examination.
6. remove any pages from question booklet.
7. write name, symbol no. in any other page than where required. Any type of indication mark places elsewhere will be breach code of conduct.
8. engage in any form of mal practice which may damage the integrity and security of NMC Licensing Examination.
9. violate the rule of NMC Licensing Examination. Candidate violating the rule will face expulsion from exam hall and may be liable for legal action.
Wednesday, August 3, 2016
Applying for Nepal Medical Council (NMC):The Online Form
Sorry for the fact that i can not uplaod all the necessary photo graph from the website because while i was applying i had no idea taht i will be writing about this. So what ever is possibel to be posted as photograph i have done it .
Which website?
Go to exams.nmc.org.np if you go to www.nmc.org.np you will never find any section
named as examination as I was bewildered among the tabs and could not find
anything where I can fill my details.
How to register?
Fill in the basics as you fill up
the first page when you join facebook. Please fill in a functioning email id
with a password you know.
Once you submit you will receive a
mail in your inbox. Open the mail and follow the link to open the NMC website.
Then only you will be able to login in the NMC site.
If you have not opened your mail,
no matter how many times you retry applying for new login account it will
report as your account has been used.
I have made my account in NMC
Website. Now What ?
Login in this site: https://exam.nmc.org.np/login.html
Now fill in the details
First page : Name, address,
marital status.
Here you need to upload your PP
sized photograph and your citizenship Certificate.
Learn what next after you get yourself registered? How to get admit card ? What else you need to know before exams.
Learn what next after you get yourself registered? How to get admit card ? What else you need to know before exams.
What documents do I need?
All the document you have presented to NMC while acquiring NMC Provisional Certificate.
Extra:
1. Six months completion letter
Which photo to upload?
Make a note that the photo you
upload here, needs to be reproduced while you appear in the exam.
So better don’t snap from your
mobile and upload it. It would be easy if your upload the scanned copy /
digital copy of PP sized photograph
How do I upload my Citizenship
Certificate ?
Better Scan or shoot the both side
of your citizenship and merge. If you upload one side of the citizenship and uploaded
the other side in the extra boxes you get in last, may be the last photo is
deleted because the last extra space is only for the certificates.
Is it necessary to scan all
documents?
I don’t know. I had upload the
photograph of each taken from my own mobile phone. But Scanned one looks good
and are better comprehensible than photos.
Can I go to Next step without
filling this page ?
NO. All the things with asterisk
mark need to be filled before you can go to next step.
How to fill other pages ?
Second page is related to your Schooling.
I don’t think it is necessary to keep the accurate date, just keep the tentative
date. I don’t think anyone is going to go to your school to verify the date and
prove you a fake doctor. Just make sure it falls on the month of Baishak and is
not Saturday. The date of complete can be mentioned as stated in the Transcript.
Third page is your higher secondary
education. Do the same as you did in Schooling section. Here you upload the
transcript and not the marks sheet of class 11 and 12.
Last page is about your MBBS. Here you need to upload all things all your
marks sheets from basic, minors and majors. They say attested copy of marks sheet
so may be it is necessary to attest the copy of marks shit and publish it.
Other things needed in this section also include letter of declaration, provisional certificate for intership, 6 months completion letter and other documents if you a foreign student.
Convert Nepali date to English in
this site : http://www.ashesh.com.np/nepali-date-converter.php
What is the letter of
declaration?
This is a page mentioning what you
have posted in this site is true to the best of your knowledge and will bear any charge if turn out to be false
and deceitful. Just go this page and download and print this page. Duly sign it
and put your thumb print, scan it and upload it.
What is MUST to complete the
last page ?
1.
Six months completion letter
2.
Letter of declaration.
3.
Provisional certificate issued by University
mentioning you are eligible to do INTERNSHIP.
They say character certificate is
must (there is an asterisk ) but you can upload all without that as well
because college won’t give you character certificate before you complete your
internship.
Provisional Number and Provisional
Certificate is only necessary when you are about to apply for exams. Just to upload
the details it is not so necessary.
The number of days of internship
can be calculated as per the letter provided to you by the college. The interval
can be measured from this site.
Can I reedit ?
Yes, you can. You can reedit datas,, value and even uploaded photographs. But once you go to apply for exam and click on payment section what ever you have posted is full and final and cannot be reedited.
Learn what next after you get yourself registered? How to get admit card ? What else you need to know before exams.
How to apply for exam ?
After you fill all the documents,
go to the exam section in the content bar and open it. There will be list (usually
one date) when you can apply for. And press apply for exams in the button in
the right hand side.
Now there will be a list of all
the information posted by you.
How to pay ?
At the end of this table there is
a button in the right hand corner saying GO FOR PAYEMENT or something like
that. After this there will be an option where there will be two menus.
- Pay via esewa: If you have e-banking activated in e-sewa compatible banks then you can transfer your amount to e-sewa and then pay via e-sewa.
- Get a token of ESEWA : if you are new to e-sewa, apply this option. Find an e-sewa centre nearby you by calling in the toll free number of E-sewa (977-1660-01-02121). Then when you find the center and give the token number along with your phone number. It will verify your number and will send you a message in the mobile.
If you are going to NMC anyways,
there is an esewa counter in the nearest proximity of NMC office in Bansghari.
So Get the token and pay out there.
Once you go for the pay section
there will a bar mentioning whether you have paid or your application is still
unpaid. Once you receive the SMS in your mobile phone it has to change to PAID.
How much to Pay ?
Nrs 2500 in normal days
NRs 3500 in the extended days with
extra charge. It is not double, just be happy . I paid this unfortunately.
Monday, August 1, 2016
Applying for Nepal Medical Council (NMC): The Provisional Certificate
This is solely based upon my personal experience and all things may
not be correct It is just to make your job hassle free and easy and it is not
an official guide. Being a medical student from Nepal I have posted all what I have actually done and don't know what International student or Nepali Student studying in Foreign need to do.
THE PROVISIONAL CERTIFICATE
When do you qualify ?
After you pass your final year exam (including Basics, Minor
and Major)
What is Provisional Certificate ?
A certificate that gives you permission to practice under
supervision (That is you can do your internship under this certicficate)
When to apply for Provisional Certificate ?
As soon as you join your internship.
Once you pass your exam, make sure that your college has sent
necessary documents to NMC stating all these students have started internship
in the college.
What document you need to apply for Provisional
Certificate?
Total 10 documents (all attested photocopies)
1.
Citizenship Certificate
|
||
School
|
2. SLC
Marksheet
|
3. Character
Certificate
|
College:
|
4. 10+2
marksheet
|
5. character
Certificate
|
University
|
6. all
3 marksheets Basics,
7. Minor
8. Major
|
9. document
from university stating you are eligible to do internship
|
10. Recent
passport Sized Photo (Atleast 4)
|
Why 4 photos?
One to fix to form .
Three photos to be provided along with form. They will fix
the same photo in all the certificates they will provide you in future (I guess,
because the same photo was there in my provisional Certificate)
Sign or write name behind each photo to be on safe side. (my
experience)
Better have 8-10 printed because though you fill an online
form, real photos need to be fixed in your admit cards (two in number).
Who can attest your documents?
Any Medical Officer with PERMANENT registration number.
(Consultants who have their permanent number, or medical Officer or Residents
who have worked for atleast 2 years and have their permanent certificates)
Better put on the stamp from the organization of the doctor
where s/he is working. So better get it done from some one in your own college
and get the stamp of the college to be on
the safe side.
Do I need to verify the duplicate and original are
equivalent ?
Better sign behind every photocopied document stating
gSsn adf]lhd ;Ssn l7s 5 . (the
duplicate is same as the original.) So that you dont have any trouble.
Who can Collect ?
Where to get the forms?NMC office at bansbari, Kathmandu
Who can Collect ?
What Forms to fill up ?
There are a total of 3 forms
1.
In Nepali Paper (Nepali kagaz) all your personal
details with a photograph
2.
One declaration form stating all statements are
true
3.
Third one also stating personal details
How to fill the form?
Fill in your details. You need to fill up your fathers name, mother name and even grand fathers name.
Citizenship certificate number, place and date of issue as well.
There are several places where you need to sign. I actually do not remember. But i think every paper has 1 place to sign and one has 2/3 places to sign so make sure all things are signed properly. (NMC called two of my friends back because they forget to sign in some of the place)
You are applying for provisional so tick on the provisional option where ever needed. Don't tick on
temporary, permanent or special.
How much to pay ?
Rs 525 worth Bank Voucher of SBI Bank. The bank is
near to NMC office at Mahargunj.
Can be paid in anyone's name and just need to attach along
with your form.
How much time does it take to process this document?
They can take as far as 2-3 months to make your provisional certificate. So better don’t take chance. We turned out unfortunate as our
college didn’t guided us adequately for this and we submitted it just 30 days
prior to our NMC exams. We just had our Certificate 1 day prior to the last day
of form submission and had to pay the extra charge on the extended deadline. It happened in 16th day, however we had to use
all our sources(from within college) to get it done in time.
Tuesday, March 15, 2016
Complete Obstetrics history (points not to be missed)
 |
| List of items in Obstetrics history |
This page is dedicated to writing history of a Obstetrics case for medical students.
The following points should always be included in any obstetrics history. These form the basis of Obstetrics history. The patient particulars followed by the presenting complains are the first things to be listed. Unlike any other history writing, obstetric history doesn't have history of present illness immediately after the chief complains. The menstrual and obstetrics history gets the priority ahead of that. Similarly, history of present pregnancy must be included before the elaboration of presenting complains because menstrual, obstetrics and history of present pregnancy is the basis of history writing in any obstetric case.
Learn more about the parity index. Para, Gravida, Living and Abortion and solve some problems.
 |
| Menstrual History : Points to include |
Learn about the indications of Cesarean Section
 |
| Previous Obstetrics history: Points to be included |
Learn more about the parity index. Para, Gravida, Living and Abortion and solve some problems.
 |
| History of present pregnancy: things you need to ask in 1st trimester |
 |
| History of present pregnancy: things you need to ask in 2nd trimester |
 |
| History of present pregnancy: things you need to ask in 3rd trimester |
Elaborate the presenting symptoms to support your provisional diagnosis, rule out the differential diagnoses with negative history and always rule out the complications associated with these problems in the history of present illness. And identify any other symptoms present that may support your diagnoses from any other systems in the body.
 |
| Things to elaborate for the presenting complains. |
Past history, Personal history, family history and socio-economic history are equally relevant and important in any history taking and so does in obstetrics.
 |
| Past medical and surgical history that needs to be taken care. |
 |
| Personal habits and history that can affect your current pregnancy. |
Including all these points mentioned in the diagram makes your history informative and complete.
Lets us see an example of a case
Monday, March 14, 2016
Congenital heart diseases and Xray signs
Long standing ASD : Handle of jug appearance
Transposition of great vessels: Egg on string sign
Type I TAPVR : figure of eight sign
TAPVR : Snowmans Heart
Partial APVR : Schmitar sign
Ebstein Anamoly: Box shaped heart
Endocardial cushion defect : Gooseneck heart
Coarctation of Aorta: figure of 3 sign
Tetralogy of Fallot: Boot shaped heart
For more reading visit http://pubs.rsna.org/doi/full/10.1148/rg.275065148
Transposition of great vessels: Egg on string sign
Type I TAPVR : figure of eight sign
TAPVR : Snowmans Heart
Partial APVR : Schmitar sign
Ebstein Anamoly: Box shaped heart
Endocardial cushion defect : Gooseneck heart
Coarctation of Aorta: figure of 3 sign
Tetralogy of Fallot: Boot shaped heart
For more reading visit http://pubs.rsna.org/doi/full/10.1148/rg.275065148
Monday, February 29, 2016
Plantar Reflexes and its equivalents with youtube video
The Normal Plantar Reflex
Nocireceptive relfexRoot value : S1
Stroking the lateral aspect of the sole with a sharp object produces (In increasing order of stimulus)
- Flexion of all five toes
- Dorsiflexion and inversion of foot (with stronger stimuli)
- Contraction of adductors of thigh, sartorius and tensor fascia lata.
Different resposnses
Normal: Flexor/Downgoing plantar reflex (as mentioned above)
Babinski Sign (Extensor/ upgoing plantar reflex)
Components of extensor reflex are
- Dorsiflexion of great toe (precedes all other movements)
- Fanning (outspreading) and extension of remaining four toes
- Dorsiflesion of ankle. flexion of knee and hip joint
- Contraction of fascia tensor lata
Equivocal/incomplete/variable response
No Response
Withdrawal reflex
Plantar Equivalents
Oppenhiems sign
Heavy pressure applied by thumb and index finger over the medial aspect of tibial (shin) from above down ward
Gordon Reflex
Squeezing or applying pressure over the calf muscle
?Shefer sign/?Schaefer Sign
Squeezing the Achilles tendon
Chaddock Sign
Striking the skin just below lateral malleolus and moving anterior /in circular fashion
Bing sign
Prinking the dorsum of foot or great toe by a pin
Moniz sign
Forceful passive flexion of ankle
Gonda sign
Forceful stretching or snapping of distal phalanges of euther the 2nd or the 4th toe
Brissauds reflex
Contraction of tensor fascia lata in amputated/absent great toe patients or complete paralysis of extensors of toe
Rossimillo Sign
Tap the ball of the foot or flick the distal phalages of toe into extension nad allow them to fall back to their normal position produces PLANTIFLEXION of ALL phalanges. (Only sign with Plantiflexion of great toe)
Equivalent of Hoffmann's Sign
Hoffmann sign
Flex the distal interpalangeal joint of the middle finger and now flick it down suddenly, response is brisk flexion and abduction of thumb as well as flexion of the other fingers.
Videos
All reflexes in one videoSources
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK397/
www.youtube.com
Harrisons Text Book Of Medicine
Bedside Clinics In Medicine 6e (Arup Kumar Kundu)
Labels:
Abnormal Reflex,
babinski Sign,
CNS Examination,
List,
Normal,
Plantar response,
Video
Strawberry Sign In Medicine
Strawberry cervix: trichomoniasis. (Trichomonas vaginalis)
erythematous cervix with pinpoint areas of exudation
Change in the gall bladder bladder wall due to excessive Cholesterol
Strawberry gingivitis/gums:
Wegener's granulomatosis: immunologically mediated uncommon multisystemdisorder affecting aerodigestive tract
SarcoidosisStrawberry nevus/hemangioma: capillary hemangioma
benign condition appearing after birth characterized by endothelial prolifeartion
Find all the terms named after Kocher
Strawberry tongue:
Glossitis with hyperplastic fungiform PapillaeScarlet Fever :GABH Streptococcus Infection
kawasaki disease: Vasculitis seen in Children
Toxic Shock Syndrome: Fatal illness caused by toxins of Staphylocccus aureus and streptococcus Pyogenes
Strawberry Shaped Nasal Mass: rhinosporidiosis
Chronic granulomatous disease caused by Rhinosporidium seeberi, characterised by production of polyps and other manifestations of hyperplasia of nasal mucosa
Strawberry skin : sarcoidosis
Strawberry shaped skull:
Edward syndrome
Edward syndrome
Trisomy 18
Sunday, February 28, 2016
KOCHERS- All terms named after Theodor Kocher
Emil Theoder Kocher was a 1909 Nobel laureate who was a swiss researcher and physician. many instruments, surgical procedures, incision used to open various parts of the body and many clinical signs has been named after him to commemorate his outstanding achievement in the field of medicine. The following are some of the terms named after him
Kocher's forcep/Clamp
It is a strong hemostatic forceps with serrated blades with interlocking teeth at the tip.
Kocher's sign
When clinician places his hands on patient’s eye and lifts it higher, patients eyelids springs up more quickly than the eyebrow, seen in Graves' Ophthalmopathy.
Kocher's incision
1. In abdomen, it is an oblique incision in right upper quadrant for open cholecystectomy.
All other surgical incisions in the abdomen.
Kocher's Maneuver:
1. Kocherisation is a surgical maneuver to expose structures in the retroperitoneum behind the duodenum and pancreas; for example to control hemorrhage from the inferior vena cava or aorta, or to facilitate removal of a pancreatic tumor.
2. In shoulder dislocation it is a maneuver used to reduce dislocations by externally rotating the shoulder, before adducting and internally rotating it.Kocher's Reflex:
It is a sign elicited as contraction of abdominal muscles, in response to testicular compression.
Kocher's vein
Kocher's Test:
The test to elicit obstruction is trachea is named as Kocher's test. Slight compression of the lateral lobe of thyroid gland produces stridor. If the test is positive, it signifies that the patient has an obstructed trachea.
Common entry point for an intraventricular catheter to drain cerebral spinal fluid from the cerebral ventricles. It is located 2.5 centimeters from the midline (at approximately the mid-pupillary line) approximately 11 cm posterior to the nasion
Kocher–Debre–Semelaigne syndrome
A type of Hypothyroidism in infancy or childhood is named as Kocher-Debre-Semelaigne Syndrome. The components of which are: lower extremity or generalized muscular hypertrophy, myxoedema, short stature and cretinism.
Exception
Though named as Kocher, the following are totally different Kochers and not to be confused with Emil Theoder Kocher.Kocher Criteria
It is a criteria to differentiate Septic Arthritis from transient synovitis in children with hip joint inflammation .It is named after Mininder S. Kocher, who was an orthopedic surgeon.
It is a incision on the skin and deep down the muslces to elbow. It is a Posterolateral Approach to Elbow allowing the exposure of the entire distal humerus as well as radial head, radial neck, and biceps tuberosity.
Kocher's interval
It is a interneural interval between the ANCONEUS and the Extensor carpi Ulnaris
Sources (SRB Textbook of surgery, Wikipedia and online resources)
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
Tags
Minor
Forensic Medicine
Difference
List
Medical notes
ENT
Mnemonic
Table
Clinical Examination
Toxicology
obstetrics
CNS Examination
Differential diagnoses
causes
history taking
student note
Case presentation. ENT
Classification
Ear
Nose
Tonsils
Undergraduate
orthopedics
Chart
DD
NMC
NMC entrance Exam
Poison
Radiology
Video
Abnormal Reflex
Cadaveric Spasm
Cinical examination
Kocher
MBBS
Nepal Medical Council
Oral Cavity
Pharynx
Tests
bloody discharge
paediatrics














