Micturition is a spinal reflex modulated by CNS.
 |
| Neural control of micturition. Source: http://physiologyplus.com/micturition-reflex-steps/ |
The pre-frontal cortex is responsible for the cognitive
control of the micturition which analyses the signals from bladder and conveys
signals according to void or not to void depending on the social setting.
The higher control of micturition is mediated by pontine
micturition centre (PMC) from where nerve fibre arise and travel along the
lateral columns bilaterally. It is the mechanical control of micturition. It
coordinates the function of baldder and sphincter.
The Sympathetic fibres are thoracolumbar (T10-L2) outflow of
nerve fibres and terminate in the hypogastric ganglion.
The Parasympathetic fibres are sacral (S2-S4) outflow.
The Parasympathetic fibres are sacral (S2-S4) outflow.
The voluntary control over the external urtheral spincter is
mediated by somatic fibres of Pudendal nerve.
Intact Spinal cord is essential for normal micturition as it
serves as a intermediate relay between the brain and the sacral center of
micturition. Sacral reflex center is the primitive voiding center which is
responsible for infants diaper need, since there is a continuous cycle of
bladder filling and voiding. The higher mental function gradually enhances in
kids as they are growing and accordingly they are trained to use toilet with
their enhanced higher mental function.
Sympathetic
|
ParaSympathetic
|
|
Bladder (Detrusor Muscle)
|
Relaxation
|
Contraction
|
Bladder Neck
|
Contarction
|
Relaxation
|
The bladder wall is relaxed and the neck constricted with
sympathetic stimulation which allows for retention of urine. The
parasympathetic stimulation causes bladder wall to contract and sphincter to
relax easing the voiding of urine.
There is a lot of analogy between skeletal muscle
contraction and bladder.
In the absence of higher control, overdistension of bladder
causes reflex detrusor contraction. Similar to the muscle
stretch reflex mediated by spindle fibre in skeletal muscle.
The upper motor neuron lesion of the brain and the spinal
cord causes features similar to that of the UMN lesion of in the muscle characterized
by Spastic bladder/ Hypertonic baldder.This is due to the reflex detrusor
contraction. There is increased tone of the detrusor muscle. However, the bladder
contracts with overdistension, the sphincter does not relax causing bladder
sphincter dyssyenrgia. This causes urgency and urge incontinence. The volume of
residual urine in the bladder is increased which causes high risk for UTI and
chronic renal failure due to obstructive uropathy. The site of the lesion is generally
the Spinal cord or pons or higher. There is no gross dilatation of the bladder
due to the reflex contraction which results in low volume high pressure inside
the bladder.
The lower motor neuron lesion to the fibre supplying bladder
causes overflow incontinence. This occurs because bladder is overdistended
however the reflex detrusor contraction doesnot comes into play. So what
happens is the bladder leaks over time when it is beyond its holding capacity
without the detrusor muscle contracting. The bladder is grossly dilated
resulting in high vomule and low ressure inside the bladder.This can be
described as flaccid or atonic bladder similar to flaccid paralysis of muscles
in LMN lesion.The patient cannot initiate the micturition. The site of injury
is generally the sacral fibres or peripheral nerve fibres
The last type of neurogenic bladder ocuurs due to injury in
the prefrontal cortex which is responsible for social control of micturition.
It allows us to find us to micturate in appropriate place. The patient doesnot
have the sense of bladder fullness. They have trouble initiating micturition
and they micturitate at inappropriate places.
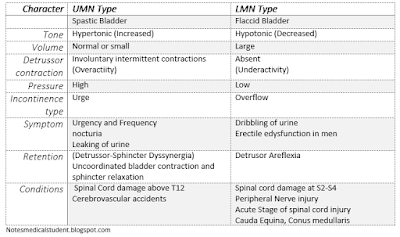
Character
|
UMN Type
|
LMN Type
|
Spastic Bladder
|
Flaccid Bladder
|
|
Tone
|
Hypertonic (Increased)
|
Hypotonic (Decreased)
|
Volume
|
Normal or small
|
Large
|
Detrussor contraction
|
Involuntary intermittent contractions
(Overactiity) |
Absent
(Underactivity) |
Pressure
|
High
|
Low
|
Incontinence type
|
Urge
|
Overflow
|
Symptom
|
Urgency and Frequency
nocturia
Leaking of urine
|
Dribbling of urine
Erectile edysfunction in men
|
Retention
|
Incomplete bladder voiding
(Detrussor-Sphincter Dyssynergia)
Uncoordinated bladder contraction and sphincter relaxation
|
Detrusor Aflexia
|
Conditions
|
Spinal Cord damage above T12
Cerebrovascular accidents
|
Spinal cord damage at S2-S4
Peripheral Nerve injury
Acute Stage of spinal cord injury
Cauda Equina, Conus medullaris
|
Source: Davidson, Merck’s Manual, Medscape